The Role of Hydrogen Fuel Cells in Sustainable Transportation
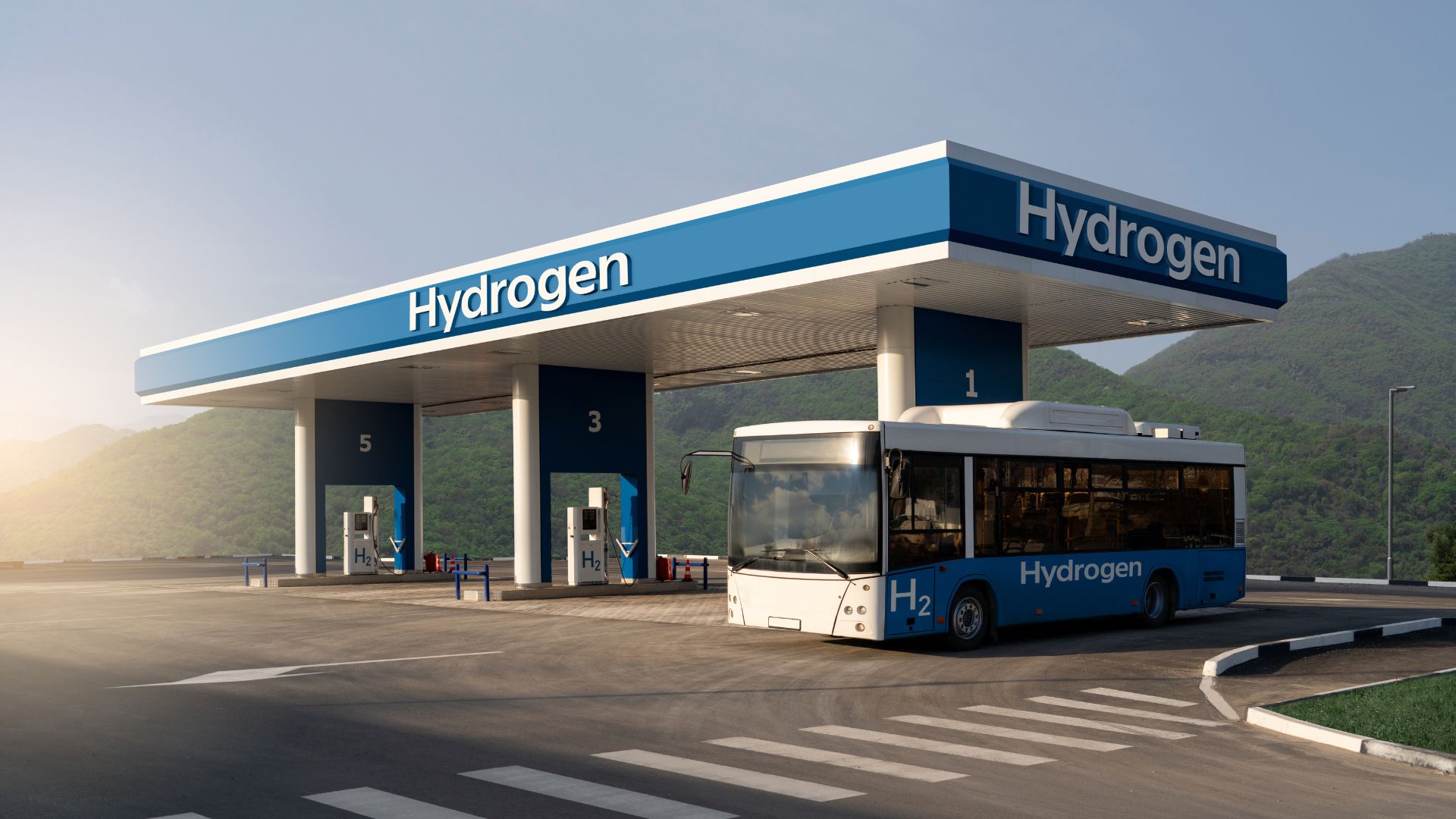

Hydrogen fuel cells are emerging as a key player in the transition toward sustainable transportation, offering a clean alternative to fossil fuels. Unlike battery-electric vehicles, hydrogen-powered vehicles generate electricity by combining hydrogen with oxygen, emitting only water vapor as a byproduct. This technology is gaining traction in various sectors, from personal cars to buses, trucks, trains, and even aircraft. With growing investments from companies like Toyota, Hyundai, and Nikola, hydrogen fuel cells are positioning themselves as a viable solution for a carbon-free future.

One of the main advantages of hydrogen fuel cells is their efficiency in long-range travel and heavy-duty applications. Unlike battery-electric vehicles, which require long charging times and have range limitations, hydrogen-powered vehicles can refuel in minutes and cover significantly greater distances. This makes them ideal for freight transport, buses, and other commercial fleets that operate continuously and require fast refueling.

However, hydrogen technology still faces infrastructure and production challenges. Hydrogen refueling stations are scarce compared to electric charging stations, making widespread adoption difficult. Additionally, most hydrogen is currently produced using fossil fuels, limiting its environmental benefits. Green hydrogen, generated through electrolysis using renewable energy, presents a promising alternative, but large-scale production remains expensive. Governments and private companies are investing in expanding hydrogen infrastructure, which could help overcome these barriers.

As advancements continue, hydrogen fuel cells have the potential to complement battery-electric vehicles, offering diverse solutions for sustainable transportation. With continued research and infrastructure development, hydrogen could play a crucial role in reducing carbon emissions and making global transportation cleaner and more efficient.